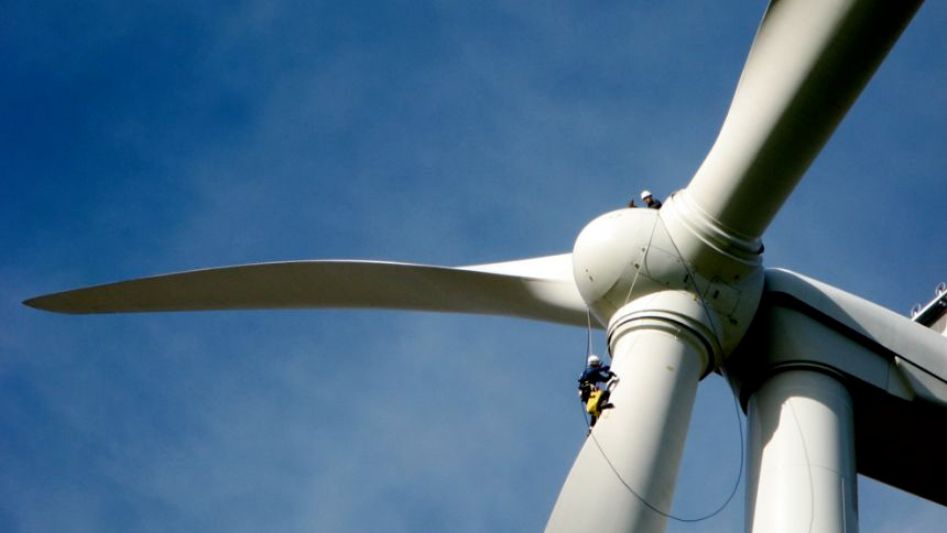
The future of wind power hangs in the balance as a heated competition unfolds between two contrasting approaches: giant turbines and radical designs. Both sides offer unique benefits and face their fair share of challenges, igniting a fierce battle for dominance in the renewable energy sector. In this article, we delve into this clash between established giants and innovative newcomers, exploring their strengths, weaknesses, and the potential implications for the future of wind power.
Table Of Content
We invite you to read: “Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: An Alternative to Traditional Wind Turbines?”
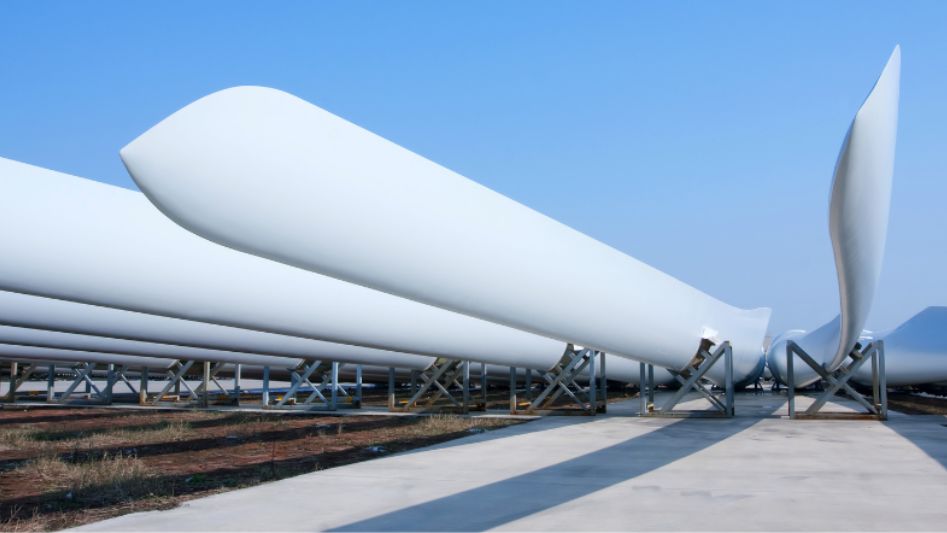

The Giant Turbines: Titans of the Wind
Giant turbines have long been the backbone of the wind power industry. These colossal structures, often towering hundreds of feet into the sky, harness the natural power of the wind to generate electricity. Here, we delve into the key characteristics and advantages of giant turbines.
Harnessing the Wind at Scale
Giant turbines are known for their impressive scale, boasting rotor diameters of up to 220 meters (721 feet) and towering heights that exceed 180 meters (590 feet). This enormous size allows them to capture wind energy more effectively, maximizing the power output.
Established Technology and Reliability
One of the primary advantages of giant turbines lies in their maturity as a technology. Over the years, extensive research and development efforts have fine-tuned these machines, making them reliable and efficient sources of renewable energy. This reliability makes giant turbines an attractive choice for investors and utilities alike.
Economies of Scale and Cost-Effectiveness
Due to their larger size, giant turbines benefit from economies of scale, enabling manufacturers to produce them more cost-effectively. This results in a lower cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity generated, making giant turbines financially viable and competitive in the energy market.
Wider Adoption and Infrastructure Support
Giant turbines have already established a strong foothold in the wind power industry. Their widespread adoption has led to the development of robust infrastructure, including specialized transport vessels for installation, maintenance teams, and established supply chains, making it easier to integrate these turbines into existing wind farms.
We invite you to read: “The Pros and Cons of Vertical Axis Wind Turbines”
The Battle for Innovation: Radical Designs Rise
While giant turbines have dominated the wind power landscape, a new wave of radical designs is challenging their supremacy. These innovative and unconventional concepts offer unique solutions to address the limitations of traditional turbines. Let’s explore the intriguing world of radical designs.
Unconventional Aesthetics and Form Factors
Radical designs often deviate from the conventional three-blade horizontal-axis design. They experiment with alternative forms, such as vertical-axis turbines, oscillating wings, or even flying wind turbines. These unconventional aesthetics aim to increase energy capture, improve efficiency, and reduce the impact on local landscapes.
Enhancing Efficiency and Adaptability
Radical designs push the boundaries of wind turbine technology by incorporating advanced features like smart materials, adjustable blades, and enhanced aerodynamics. These innovations seek to optimize energy conversion and adapt to varying wind conditions, ultimately increasing the overall efficiency of the turbines.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
In addition to performance improvements, radical designs also strive to address environmental concerns associated with wind power. Some concepts focus on reducing noise pollution, while others explore ways to minimize the impact on wildlife, including birds and bats. These considerations play a crucial role in ensuring sustainable and responsible wind power development.
Exploring New Frontiers with Offshore and Floating Solutions
As land-based wind farms face space constraints, radical designs have ventured into offshore and floating solutions. These designs unlock the vast potential of wind resources in coastal areas and open sea regions, where stronger and more consistent winds prevail. Offshore wind farms are also less visible from the shore, minimizing potential aesthetic objections.
We invite you to read: “Harnessing the Wind: An Introduction to Wind Turbines and Wind Energy”

Conclusion
As the world grapples with the need for clean and sustainable energy sources, the battle between giant turbines and radical designs in the wind power industry intensifies. While giant turbines have established themselves as reliable and cost-effective, radical designs offer innovative solutions and potential advancements in efficiency. The clash between these two approaches will ultimately shape the future of wind power. As we navigate this battle, it is essential to strike a balance between established technologies and the pursuit of innovation. By doing so, we can harness the full potential of wind energy and drive the transition toward a greener future.
FAQ
What are the main advantages of giant turbines over radical designs?
Giant turbines offer established technology, reliability, and economies of scale. Their larger size allows for capturing more wind energy, and their widespread adoption has resulted in well-developed infrastructure and supply chains.
How do radical designs aim to overcome the limitations of giant turbines?
Radical designs explore unconventional aesthetics, enhanced efficiency through advanced features, and address environmental concerns. They also venture into offshore and floating solutions to tap into new wind resources.
Are giant turbines more cost-effective than radical designs?
Due to economies of scale, giant turbines often have a lower cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity generated. However, radical designs aim to improve efficiency and reduce costs through technological advancements.
What are the challenges faced by radical designs?
Radical designs often encounter challenges related to technological feasibility, scalability, and market acceptance. Overcoming these hurdles requires extensive research, development, and testing.
You May Also Like
- The Power of Aerodynamics: Lessons from Wind Turbines and Formula 1 Cars
- The Benefits of Implementing Vertical Axis Wind Turbines Offshore
- Wind Power at its Best: The Future of Energy Generation with Kite Turbines
- Martian Wind Energy: A Science Fiction Look at the Possibility of Wind Turbines on Mars
- The Sky’s the Limit: Understanding the Potential of Kite Turbines for Wind Energy

